
MO3 - a file format, encapsulating the features of several "MOD" formats (IT, XM, S3M, MTM, MOD, MPTM), but with one big difference: MP3 and OGG compressed samples.The tracker has numerous additional effects.
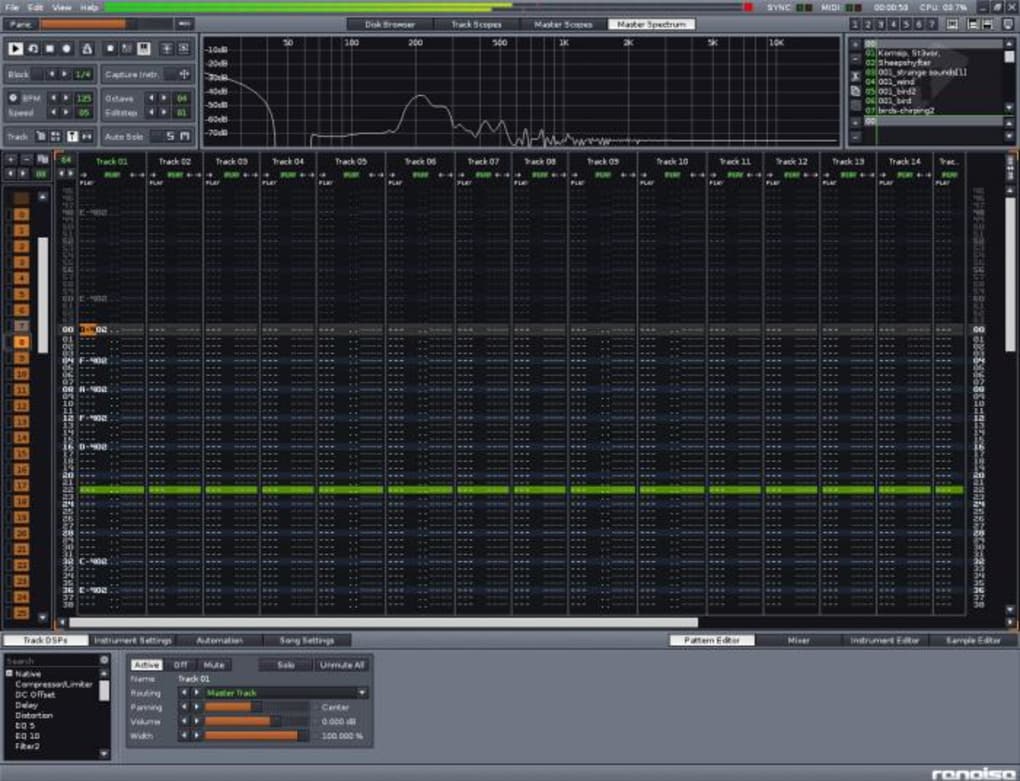
The format supports up to 8 channels, hence the name, and up to 36 samples.
GOATTRACKER RENOISE MOD
Both formats are based on the original MOD format used on the Commodore Amiga computer.
GOATTRACKER RENOISE SOFTWARE
Those who produce these files (using the software called music trackers) and listen to them, form the worldwide MOD scene, a part of the demoscene subculture. - MOD music, or tracker music are a family of music file formats originating from the MOD file format on Amiga systems used in the late 1980s.Mod files are read, indexed and all samples are hashed, this in turn allows this page to cross-reference the samples.All samples are stored and hashed in raw format. Usually made in SoundTracker, Protracker. - This is an page indexing Amiga Music Modules of the MOD file format.
Tracker History Graphing Project - Inspired by the UNIX History Graphing Project, the objective is to collect release dates and dependencies of music trackers and produce a graph of the lineage of music trackers in different operating systems.Ultimate Soundtracker, ProTracker, Scream Tracker, Fast Tracker, Impulse Tracker, Renoise. Ultimate Music Tracker Base - Comprehensive database of music tracking software.Later trackers departed from module file limitations and advantages, adding other options both to the sound synthesis (hosting generic synthesizers and effects or MIDI output) and to the sequencing (MIDI input and recording), effectively becoming general purpose sequencers with a different user interface. Separate patterns have independent timelines a complete song consists of a master list of repeated and concatenated patterns. The file format used for saving songs is called a module file.Ī music tracker's musical interface is traditionally numeric: both notes and parameter changes, effects and other commands are entered with the keyboard into a grid of fixed time slots as codes consisting of letters, numbers and hexadecimal digits. They represent music tracks as an arrangement of discrete musical notes positioned in one of several channels, at discrete chronological positions on a timeline.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
